Bevy Traditional Roguelike Quick-Start - 4. À la Carte Sorcery
With our only unique skill of note being moving around, it's hard to feel emotionally invested in these poor critters running in circles forever in an unbreakable cage. An inevitable component of fantasy gaming is required: magic.
Now, with the way the system is currently set up, "pressing this button to dash forwards 4 spaces" would be extremely easy. We can do better - a system which would normally be painful to implement, but which takes advantage of Rust's pattern matching and enums, as well as Bevy's system ordering... Enter - Spell Crafting.
Design Capsule
Spells will be composed of a series of Forms and Functions. Forms choose tiles on the screen, and Functions execute an effect on those tiles. In the case of a lasso, for example, the Form is a projectile and the Function is getting constricted.
Create a new file, spells.rs.
// spells.rs
use bevy::prelude::*;
pub struct SpellPlugin;
impl Plugin for SpellPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {}
}
Don't forget to link it into main.rs.
// main.rs
// SNIP
mod spells;
// SNIP
use spells::SpellPlugin;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(ImagePlugin::default_nearest()))
.add_plugins((
SpellPlugin, // NEW!
EventPlugin,
GraphicsPlugin,
MapPlugin,
InputPlugin,
))
.run();
}
D.I.Y. Wizard
Now, we may start to populate this new plugin with some starting structs and enums. I named the individual components that form a Spell "Axiom" because:
- Calling them "Components" would get confusing fast with Bevy components.
- They are things that happen, an enforceable truth.
- The word "Axiom" is just dripping with flair and style.
// spells.rs
#[derive(Event)]
/// Triggered when a creature (the `caster`) casts a `spell`.
pub struct CastSpell {
pub caster: Entity,
pub spell: Spell,
}
#[derive(Component, Clone)]
/// A spell is composed of a list of "Axioms", which will select tiles or execute an effect onto
/// those tiles, in the order they are listed.
pub struct Spell {
pub axioms: Vec<Axiom>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
/// There are Form axioms, which target certain tiles, and Function axioms, which execute an effect
/// onto those tiles.
pub enum Axiom {
// FORMS
/// Target the caster's tile.
Ego,
// FUNCTIONS
/// The targeted creatures dash in the direction of the caster's last move.
Dash { max_distance: i32 },
}
We will begin with the very simple spell "Ego, Dash". When cast, the caster dashes in the direction of their last move. Note that I didn't use "Self" for the self-target, because it's already taken by Rust as a keyword, and "Ego" sounds very cool.
The implementation will rely on a struct with yet another cute name: Synapses. Named after the transmission of signals between neurons, they are like a snowball rolling down a hill and accumulating debris.
When a new SynapseData is created, it is blank except for the fact that it knows its caster. It still has no tiles to target (targets is an empty vector), and is on the first step of its execution (step is 0). As it "rolls" down the list of Axioms, it will accumulate targets - tiles where the spell effect happen.
// spells.rs
/// The tracker of everything which determines how a certain spell will act.
struct SynapseData {
/// Where a spell will act.
targets: Vec<Position>,
/// How a spell will act.
axioms: Vec<Axiom>,
/// The nth axiom currently being executed.
step: usize,
/// Who cast the spell.
caster: Entity,
}
impl SynapseData {
/// Create a blank SynapseData.
fn new(caster: Entity, axioms: Vec<Axiom>) -> Self {
SynapseData {
targets: Vec::new(),
axioms,
step: 0,
caster,
}
}
/// Get the Entity of each creature standing on a tile inside `targets` and its position.
fn get_all_targeted_entity_pos_pairs(&self, map: &Map) -> Vec<(Entity, Position)> {
let mut targeted_pairs = Vec::new();
for target in &self.targets {
if let Some(creature) = map.get_entity_at(target.x, target.y) {
targeted_pairs.push((*creature, *target));
}
}
targeted_pairs
}
}
Each ̀synapse is like a customer at a restaurant - when a spell is cast, it is added to a SpellStack. The most recently added spells are handled first, which is not the hallmark of great customer service. This is because spells will later be capable of having chain reactions...
For example, dashing onto a trap which triggers when it is stepped on should resolve the trap effects before continuing with the dash spell.
// spells.rs
pub fn cast_new_spell(
mut cast_spells: EventReader<CastSpell>,
mut spell_stack: ResMut<SpellStack>,
) {
for cast_spell in cast_spells.read() {
// First, get the list of Axioms.
let axioms = cast_spell.spell.axioms.clone();
// Create a new synapse to start "rolling down the hill" accumulating targets and
// dispatching events.
let synapse_data = SynapseData::new(cast_spell.caster, axioms);
// Send it off for processing - right away, for the spell stack is "last in, first out."
spell_stack.spells.push(synapse_data);
}
}
Each tick, we'll get the most recently added spell, and where it currently is in its execution (its step). We'll get the corresponding ̀Axiom - for example, being at step 0 in [Axiom::Ego, Axiom::Dash] will result in running Axiom::Ego. Then, we'll run a matching one-shot system - a Bevy feature I will soon demonstrate.
// spells.rs
/// Get the most recently added spell (re-adding it at the end if it's not complete yet).
/// Get the next axiom, and runs its effects.
pub fn process_axiom(
mut commands: Commands,
axioms: Res<AxiomLibrary>,
spell_stack: Res<SpellStack>,
) {
// Get the most recently added spell, if it exists.
if let Some(synapse_data) = spell_stack.spells.last() {
// Get its first axiom.
let axiom = synapse_data.axioms.get(synapse_data.step).unwrap();
// Launch the axiom, which will send out some Events (if it's a Function,
// which affect the game world) or add some target tiles (if it's a Form, which
// decides where the Functions will take place.)
commands.run_system(*axioms.library.get(&discriminant(axiom)).unwrap());
// Clean up afterwards, continuing the spell execution.
commands.run_system(spell_stack.cleanup_id);
}
}
But first, how do we match the Axiom with the corresponding one-shot system? It uses mem::discriminant - which should be imported right away, and an AxiomLibrary resource.
// spells.rs
#[derive(Resource)]
/// All available Axioms and their corresponding systems.
pub struct AxiomLibrary {
pub library: HashMap<Discriminant<Axiom>, SystemId>,
}
impl FromWorld for AxiomLibrary {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
let mut axioms = AxiomLibrary {
library: HashMap::new(),
};
axioms.library.insert(
discriminant(&Axiom::Ego),
world.register_system(axiom_form_ego),
);
axioms.library.insert(
discriminant(&Axiom::Dash { max_distance: 1 }),
world.register_system(axiom_function_dash),
);
axioms
}
}
We use discriminants, because each Axiom can possibly have extra fields like max_distance, and we wish to differentiate them by variant regardless of their inner contents. We link each one with its own one-shot system, currently axiom_form_ego and axiom_function_dash. These systems - which are not yet implemented - are registered into the World, Bevy's term for the struct which contains... well, everything. Each time a ̀Query is ran, behind the scenes, it reaches into the World to look up entities similarly to SQL queries!
Now, for the SpellStack:
// spells.rs
#[derive(Resource)]
/// The current spells being executed.
pub struct SpellStack {
/// The stack of spells, last in, first out.
spells: Vec<SynapseData>,
/// A system used to clean up the last spells after each Axiom is processed.
cleanup_id: SystemId,
}
impl FromWorld for SpellStack {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
SpellStack {
spells: Vec::new(),
cleanup_id: world.register_system(cleanup_last_axiom),
}
}
}
One more one-shot system to be implemented later, cleanup_last_axiom. Let's get started with ̀Ego and Dash's one-shot systems. Called with commands.run_system, these are detached from the scheduled Startup and Update, being ran only when demanded. They will never be ran in parallel with another system, which can, in some cases, be a performance bottleneck - but it's exactly what we need for this use-case.
// spells.rs
/// Target the caster's tile.
fn axiom_form_ego(
mut spell_stack: ResMut<SpellStack>,
position: Query<&Position>,
) {
// Get the currently executed spell.
let synapse_data = spell_stack.spells.last_mut().unwrap();
// Get the caster's position.
let caster_position = *position.get(synapse_data.caster).unwrap();
// Add that caster's position to the targets.
synapse_data.targets.push(caster_position);
}
Dashing is a significantly more involved process. For each creature standing on a tile targeted by a Form (in this case, the Player only - Ego is cast by the Player, and selects itself), they are commanded to dash in the direction of the Player's last step. This is done by effectively shooting a "beam" forwards, propagating through empty tiles until it hits an impassable one.
// spells.rs
/// The targeted creatures dash in the direction of the caster's last move.
fn axiom_function_dash(
mut teleport: EventWriter<TeleportEntity>,
map: Res<Map>,
spell_stack: Res<SpellStack>,
momentum: Query<&OrdDir>,
) {
let synapse_data = spell_stack.spells.last().unwrap();
let caster_momentum = momentum.get(synapse_data.caster).unwrap();
if let Axiom::Dash { max_distance } = synapse_data.axioms[synapse_data.step] {
// For each (Entity, Position) on a targeted tile with a creature on it...
for (dasher, dasher_pos) in synapse_data.get_all_targeted_entity_pos_pairs(&map) {
// The dashing creature starts where it currently is standing.
let mut final_dash_destination = dasher_pos;
// It will travel in the direction of the caster's last move.
let (off_x, off_y) = caster_momentum.as_offset();
// The dash has a maximum travel distance of `max_distance`.
let mut distance_travelled = 0;
while distance_travelled < max_distance {
distance_travelled += 1;
// Stop dashing if a solid Creature is hit and the dasher is not intangible.
if !map.is_passable(
final_dash_destination.x + off_x,
final_dash_destination.y + off_y,
)
{
break;
}
// Otherwise, keep offsetting the dashing creature's position.
final_dash_destination.shift(off_x, off_y);
}
// Once finished, release the Teleport event.
teleport.send(TeleportEntity {
destination: final_dash_destination,
entity: dasher,
});
}
} else {
// This should NEVER trigger. This system was chosen to run because the
// next axiom in the SpellStack explicitly requested it by being an Axiom::Dash.
panic!()
}
}
This is almost perfect, aside from the fact that we have absolutely no idea what the Player's last step direction was... And that's what OrdDir is for!
Weaving Magic From Motion (OrdDir momentum component)
OrdDir already exists, but it is currently nothing but a simple enum. It could be elevated into a much greater Component...
// main.rs
#[derive(Component, PartialEq, Eq, Copy, Clone, Debug)] // CHANGED: Added Component.
pub enum OrdDir {
Up,
Right,
Down,
Left,
}
It will also need to be a crucial part of each Creature.
// creature.rs
#[derive(Bundle)]
pub struct Creature {
pub position: Position,
pub momentum: OrdDir, // NEW!
pub sprite: Sprite,
}
This will instantly rain down errors into the crate - all Creatures must now receive this new Component.
// map.rs
fn spawn_player(
mut commands: Commands,
asset_server: Res<AssetServer>,
atlas_layout: Res<SpriteSheetAtlas>,
) {
// SNIP
..default()
},
momentum: OrdDir::Up, // NEW!
},
Player,
));
}
fn spawn_cage(
mut commands: Commands,
asset_server: Res<AssetServer>,
atlas_layout: Res<SpriteSheetAtlas>,
) {
// SNIP
..default()
},
momentum: OrdDir::Up, // NEW!
});
if tile_char == 'H' {
creature.insert(Hunt);
}
}
}
All good, but all Creatures are now eternally "facing" upwards regardless of their actions. Let us adjust this, at least for only the Player... for now.
// events.rs
fn player_step(
mut events: EventReader<PlayerStep>,
mut teleporter: EventWriter<TeleportEntity>,
mut player: Query<(Entity, &Position, &mut OrdDir), With<Player>>, // CHANGED - mutable, and with &mut OrdDir
hunters: Query<(Entity, &Position), With<Hunt>>,
map: Res<Map>,
) {
let (player_entity, player_pos, mut player_momentum) // CHANGED - New mutable player_momentum
= player.get_single_mut().expect("0 or 2+ players"); // CHANGED - get_single_mut
// SNIP
teleporter.send(TeleportEntity::new(
player_entity,
player_pos.x + off_x,
player_pos.y + off_y,
));
// NEW!
// Update the direction towards which this creature is facing.
*player_momentum = event.direction;
// End NEW.
for (hunter_entity, hunter_pos) in hunters.iter() {
// SNIP
}
}
}
The Cleanup
Remember this? commands.run_system(spell_stack.cleanup_id); Running Axioms is fine and all, but we'll also want to progress through the list so we aren't stuck selecting the player's tile for eternity.
fn cleanup_last_axiom(mut spell_stack: ResMut<SpellStack>) {
// Get the currently executed spell, removing it temporarily.
let mut synapse_data = spell_stack.spells.pop().unwrap();
// Step forwards in the axiom queue.
synapse_data.step += 1;
// If the spell is finished, do not push it back.
if synapse_data.axioms.get(synapse_data.step).is_some() {
spell_stack.spells.push(synapse_data);
}
}
The step advances, and the spell is removed if it is finished. Therefore, a typical spell would run like this:
- Step 0, run Ego. Select the Player.
- Cleanup. Move to step 1, the spell isn't finished yet.
- Step 1, run Dash. The Player teleports.
- Cleanup, Move to step 2. There is no Axiom at index 2, and the spell is deleted.
The Test Run
After all this, the first spell Ego, Dash is ready to enter our grimoire - and while that was a lot, future spell effects will be a lot easier to implement from now on. Simply add more entries in the AxiomLibrary with one-shot systems to match!
One last thing: actually casting it.
// input.rs
/// Each frame, if a button is pressed, move the player 1 tile.
fn keyboard_input(
player: Query<Entity, With<Player>>, // NEW!
mut spell: EventWriter<CastSpell>, // NEW!
mut events: EventWriter<PlayerStep>,
input: Res<ButtonInput<KeyCode>>,
) {
// NEW!
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::Space) {
spell.send(CastSpell {
caster: player.get_single().unwrap(),
spell: Spell {
axioms: vec![Axiom::Ego, Axiom::Dash { max_distance: 5 }],
},
});
}
// End NEW.
// SNIP
}
Finally, cargo ruǹ will allow us to escape the sticky grasp of the Hunter by pressing the spacebar! What's that? It crashed? Of course, we now need to register absolutely everything that was just added into Bevy's ECS.
This is extremely easy to forget and is mostly indicated by "struct is never constructed"-type warnings. If you are ever testing your changes and things seem to be going wrong, check first that you registered your systems, events and resources!
With that said:
// spells.rs
impl Plugin for SpellPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.add_event::<CastSpell>();
app.init_resource::<SpellStack>();
app.init_resource::<AxiomLibrary>();
app.add_systems(Update, cast_new_spell);
app.add_systems(Update, process_axiom);
}
}
And there's just one last thing I'd like to change for now: knocking down the light-speed movement down a notch.
// input.rs
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::KeyW) { // CHANGED to just_pressed
events.send(PlayerStep {
direction: OrdDir::Up,
});
}
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::KeyD) { // CHANGED to just_pressed
events.send(PlayerStep {
direction: OrdDir::Right,
});
}
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::KeyA) { // CHANGED to just_pressed
events.send(PlayerStep {
direction: OrdDir::Left,
});
}
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::KeyS) { // CHANGED to just_pressed
events.send(PlayerStep {
direction: OrdDir::Down,
});
}
Try again. cargo run. Pressing the space bar will now allow you to escape your sticky little friend!
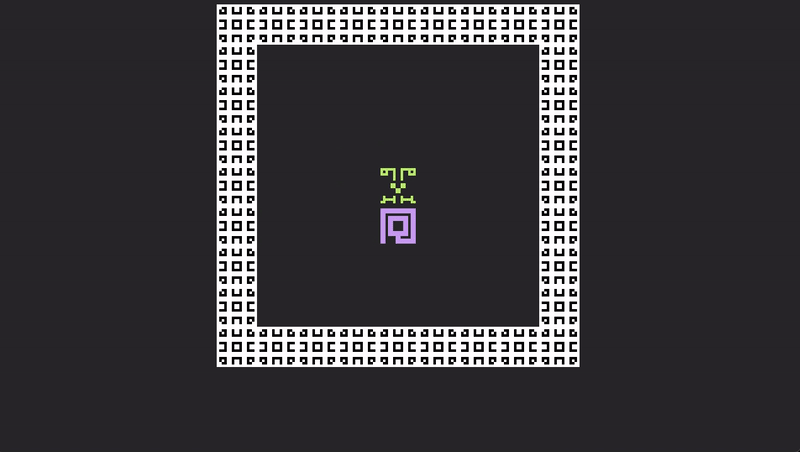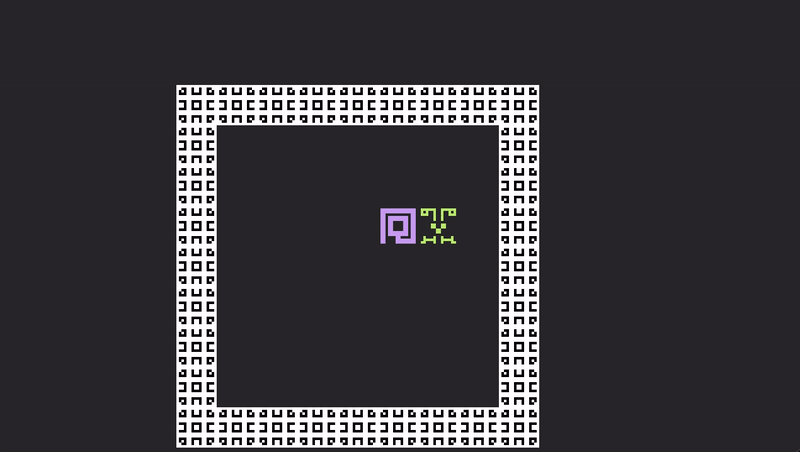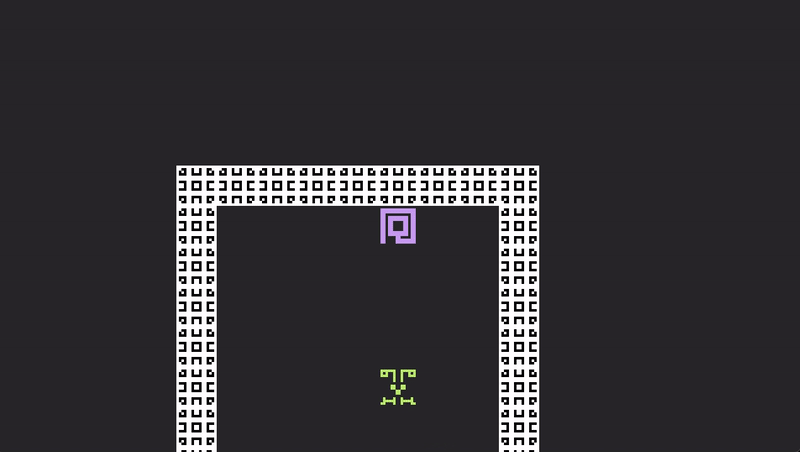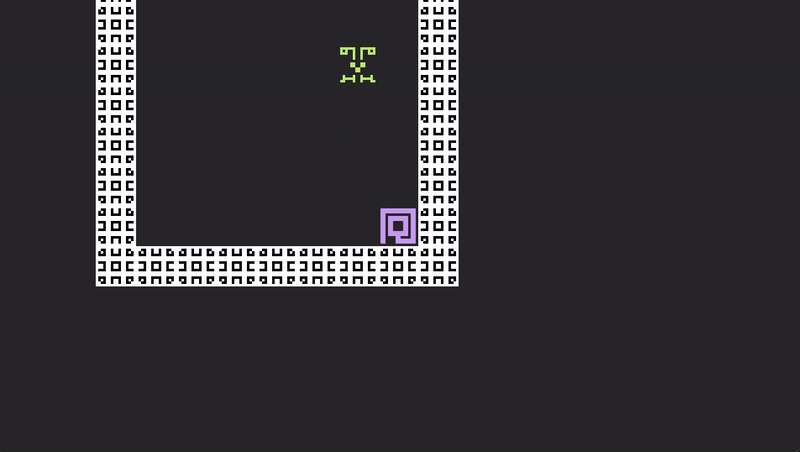
Intermediate Wizardry 201
The player dashing around is fun and good... but what about a projectile that knocks back whatever critter it hits? This sounds slightly far-fetched, but it actually takes almost no code that we have not already seen. Enter... MomentumBeam, Dash.
// spells.rs
pub enum Axiom {
// FORMS
/// Target the caster's tile.
Ego,
// NEW!
/// Fire a beam from the caster, towards the caster's last move. Target all travelled tiles,
/// including the first solid tile encountered, which stops the beam.
MomentumBeam,
// End NEW.
// SNIP
}
It, of course, receives its own implementation.
/// Fire a beam from the caster, towards the caster's last move. Target all travelled tiles,
/// including the first solid tile encountered, which stops the beam.
fn axiom_form_momentum_beam(
map: Res<Map>,
mut spell_stack: ResMut<SpellStack>,
position_and_momentum: Query<(&Position, &OrdDir)>,
) {
let synapse_data = spell_stack.spells.last_mut().unwrap();
let (caster_position, caster_momentum) =
position_and_momentum.get(synapse_data.caster).unwrap();
// Start the beam where the caster is standing.
// The beam travels in the direction of the caster's last move.
let (off_x, off_y) = caster_momentum.as_offset();
let mut output = linear_beam(*caster_position, 10, off_x, off_y, &map);
// Add these tiles to `targets`.
synapse_data.targets.append(&mut output);
}
fn linear_beam(
mut start: Position,
max_distance: usize,
off_x: i32,
off_y: i32,
map: &Map,
) -> Vec<Position> {
let mut distance_travelled = 0;
let mut output = Vec::new();
// The beam has a maximum distance of max_distance.
while distance_travelled < max_distance {
distance_travelled += 1;
start.shift(off_x, off_y);
// The new tile is always added, even if it is impassable...
output.push(start);
// But if it is impassable, the beam stops.
if !map.is_passable(start.x, start.y) {
break;
}
}
output
}
You may notice that this is extremely similar to the Dash logic... Its differences are the inclusion of the final impact tile (which is solid), and how it collects all travelled tiles in an output vector, added to targets.
// Do not add this block, it is already included.
let mut distance_travelled = 0;
while distance_travelled < max_distance {
distance_travelled += 1;
// Stop dashing if a solid Creature is hit and the dasher is not intangible.
if !map.is_passable(
final_dash_destination.x + off_x,
final_dash_destination.y + off_y,
)
{
break;
}
// Otherwise, keep offsetting the dashing creature's position.
final_dash_destination.shift(off_x, off_y);
}
In software development, "don't repeat yourself" is a common wisdom, but in games development, sometimes, it must be done within reason. There might be intangible creatures later capable of moving through solid blocks (a purely theoretical concern which will totally not be the subject of a future chapter). In this case, their dashes must move through walls, and their beams must not.
Back to the implemention. Add this new Axiom to the AxiomLibrary.
impl FromWorld for AxiomLibrary {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
// SNIP
// NEW!
axioms.library.insert(
discriminant(&Axiom::MomentumBeam),
world.register_system(axiom_form_momentum_beam),
);
// End NEW.
// SNIP
}
}
And just like that, with only 1 new one-shot-system (which was very similar to our Dash implementation), the projectile is ready:
// input.rs
if input.just_pressed(KeyCode::Space) {
spell.send(CastSpell {
caster: player.get_single().unwrap(),
spell: Spell {
axioms: vec![Axiom::MomentumBeam, Axiom::Dash { max_distance: 5 }],
},
});
}
cargo run. Not only can you teach your sticky companion some manners, you can even break the walls of the cage, and escape into the abyss beyond.